Welcome to our Knowledge Base
DIRECT AND INVERSE PROPORTIONS
- Two quantities x and y are said to be in direct proportion if they increase or decrease together in such a manner that the ratio of
their corresponding values remain constant. That is, x/y = = k where
- k is a positive number if x and y are in direct proportion or vary directly. In case of direct proportion, if y1, y2 are the values of y
corresponding to the values x1, x2 of x respectively, then
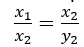
- Two quantities x and y are said to be in inverse proportion if an increase in x causes a proportional decrease in y and vice-versa, in such a manner that the product of their corresponding values remains constant. That is, xy = k where k is a positive number, if x and y are in inverse proportion. In this case, if y1, y2 are the values of y corresponding to the values x1, x2 of x respectively, then x1 y1=x2y2,
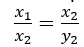
- Quantities increasing or decreasing together need not always be in direct proportion, same in the case of inverse proportion.
- When two quantities x and y are in direct proportion (or vary directly), they are written as x ∝ y. Symbol “∝” stands for ‘is proportional to’.
- When two quantities x and y are in inverse proportion (or vary inversely) they are written as x ∝1/y