Introduction to Light
How do we see objects?
When a beam of light falls on an object from the source of light (mainly, sun) then this light gets reflected in all directions after striking that object. The reflected light then reaches our eyes, and our brain interprets the object. It’s harder to see at night as there’s less light to bounce off objects.
Some facts about light
Laws of Reflection
The phenomenon of light bouncing off surfaces is called reflection.
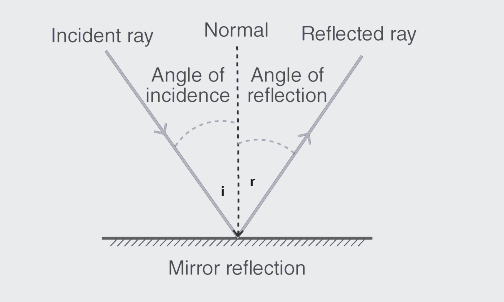
In short the principle when the light rays fall on the smooth surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, also the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
Regular and Diffused Reflection
When parallel rays are incident on a surface, the reflected ray will also be in parallel if the surface of reflection is a regular surface. But if the surface is irregular surface, the reflected rays will not be in parallel, and this is known as irregular or diffused reflection.
Multiple reflection
We can get multiple reflections if we keep 2 mirror at an angle. This will result in formation of multiple images depending on the angle between them.
If the mirrors are placed in parallel, then there will be infinite images.
Number of images formed=(360/Angle between the mirrors) – 1
Dispersion of Light
The splitting of light into its component colours is called dispersion. Eg: Rainbow, dispersion using Prism
Uses of Reflection
Human Eye
Different parts of Human eye:
Cornea – Light is focused primarily by the Cornea, which is the clear front of the eye. Cornea acts like a camera lens for the human eye.
Iris – The Iris of the eye controls the amount of light reaching the back of the eye, by automatically adjusting the size of the aperture.
Eye lens – The eye’s crystalline lens is located directly behind the pupil and further focuses light.
Pupil – The pupil is a hole located in the center of the Iris of the eye which allows the light to strike the retina.
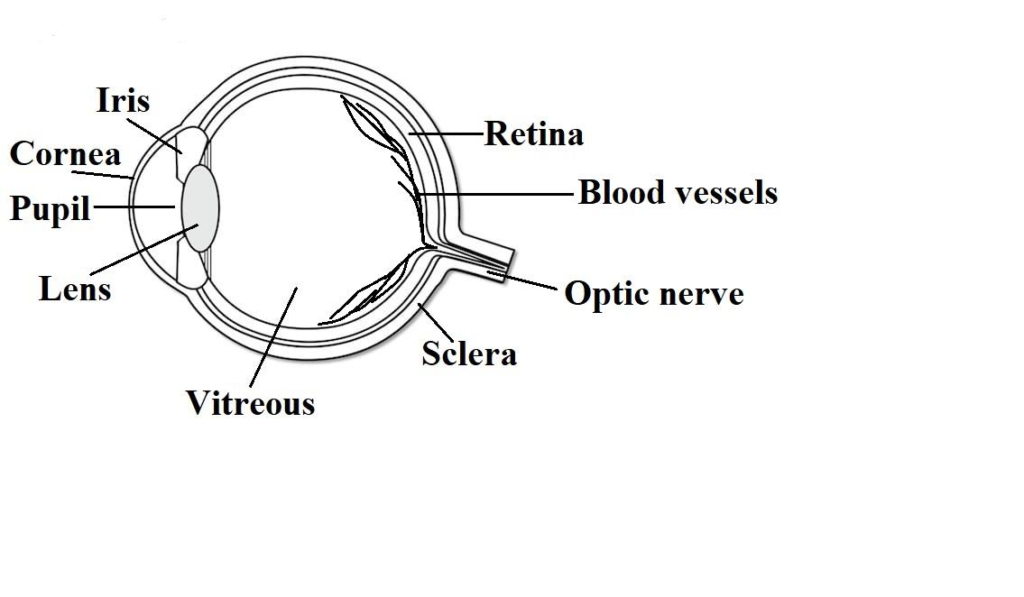
Retina – Light focused by the cornea and crystalline lens then reaches the retina, the light sensitive inner lining of the back of the eye. The purpose of the retina is to receive the light focused by the lens, converting it into neural signals and sending these signals to the brain for visual recognition.
Sclera – It is the opaque, fibrous, protective, outer layer of the human eye containing mainly collagen and some elastic fibre.
Blood vessels – Blood vessels provide blood to the eye and veins drain blood from the eye.
Vitreous – It is a gel like structure that fills the interior of the eye and helps to preserve its round shape.
Optic nerve – Optic nerves transfer visual information from the retina to the vision centres of the brain via electrical impulses.