Introduction to Chemical Effect of Electric Current
The chemical reaction that takes place in a conducting solution when an electric current is passed through it is called the chemical effect of electric current.
Side note – William Nicholson discovered the electrolysis of water
Some of the visible chemical effects of electric current as a result of passing electric current through a conducting solution are
- Gas bubbles that are formed at electrodes
- Metals deposited on electrodes
- Change of colour of solutions
Before we go into details of chemical effects, we should know few terms so that it is easier to understand.
Conductor -Conductors are substance which allows free flow of heat or electricity. It can be classified as good or bad. Good conductor allows flow of electricity or heat e.g. copper, aluminium, steel etc. Bad conductor do not allow flow of electricity or heat e.g. Wood, plastic, pure water etc.
Electrodes – A conductor, when immersed during a solution with its end connected to the terminals of a battery, thereby completing a circuit, is named an electrode. There are usually 2 electrodes→ cathode(-ve) and anode(+ve).
Electrolytes – An electrolyte is a solution in which the electrodes are submerged. They dissociate on the passage of electric current.
What happens when electricity is passed through conducting solution?
As we have seen earlier there are some visible effects like forming of gas bubbles at electrodes, metals deposited on electrodes or change in colours. All these will depend on the solution and the electrodes used.
When electricity is passed through water mixed with different substances, the constituents break into negative and positive ions. These ions pass an electric current through them. The more the number of ions, the better the conductor of electricity it is.
Experiment 1 – Demonstrate conduction of electricity in liquid
Items required – A cell/battery, Connecting wires, LED/bulb, solution
Observations:
Above process is also called an electrolysis.
Applications of Electrolysis
Electroplating
Electroplating is a process where a layer of metal is deposited on another material with the help of electricity.
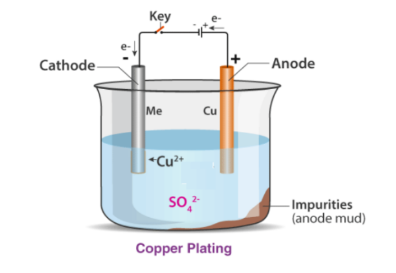
While coating copper over brass, you need a copper electrode and a brass electrode and any solution containing copper, such as copper sulphate solution. The copper electrode is made anode, and the brass electrode is made the cathode. When current is passed through the copper sulphate solution, it breaks down into ions. The copper ions with a positive charge get attracted to the brass electrode, and the sulphur ions with a negative charge get attracted to copper electrode. The amount of time taken for the completion of the process depends upon the strength of the being passed through the circuit and the concentration of the solution.
Similarly, depending on requirement choice of solution, anode and cathode will vary.
Various applications of electroplating
Extracting Metals from their Ores
When electricity is passed through metal ores, they get broken down into ionic lattices. This way, the metals are extracted separately. Metals such as sodium, calcium, potassium, aluminium and magnesium are obtained from their ores using this method.
Purification of metals
Electrolysis is used in the purification of metals by extracting impurities from them. The impure metal is used as an anode in the process and is dissolved in the electrolyte solution. The metal ions are deposited on the cathode during the process, and a pure form of metal is obtained here. The impurities remain in the electrolyte solution. Metals such as zinc, copper, aluminium and copper are purified this way.
Production of Compounds
Electrolysis is helpful in producing some compounds, such as sodium hypochlorite.
Decomposition of Compounds
Electrolysis is used to decompose a compound into its constituents. Water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis.